Identifying novel factors associated with COVID-19 transmission and fatality using the machine learning approach
Mengyuan Li 1, 2, Zhilan Zhang 1, 2, Wenxiu Cao 1, 2, Yijing Liu 3, Beibei Du 3, Canping Chen 1, 2, Qian Liu 1, 2, Md. Nazim Uddin 1, 2, Shanmei Jiang 1, 2,Cai Chen 4, Yue Zhang 5, 6, 7, Xiaosheng Wang 1,
1 Biomedical Informatics Research Lab, School of Basic Medicine and Clinical Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 211198, China
2 Big Data Research Institute, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 211198, China
3 School of Life Science and Technology, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 211198, China
4 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA.
5 Futian Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Shenzhen 518000, China
6 Pinghu hospital of Shenzhen university, Shenzhen 440307, China
7 Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The First Clinical college of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, China *
Correspondence to: Xiaosheng Wang, E-mail: xiaosheng.wang@cpu.edu.cn
Abstract
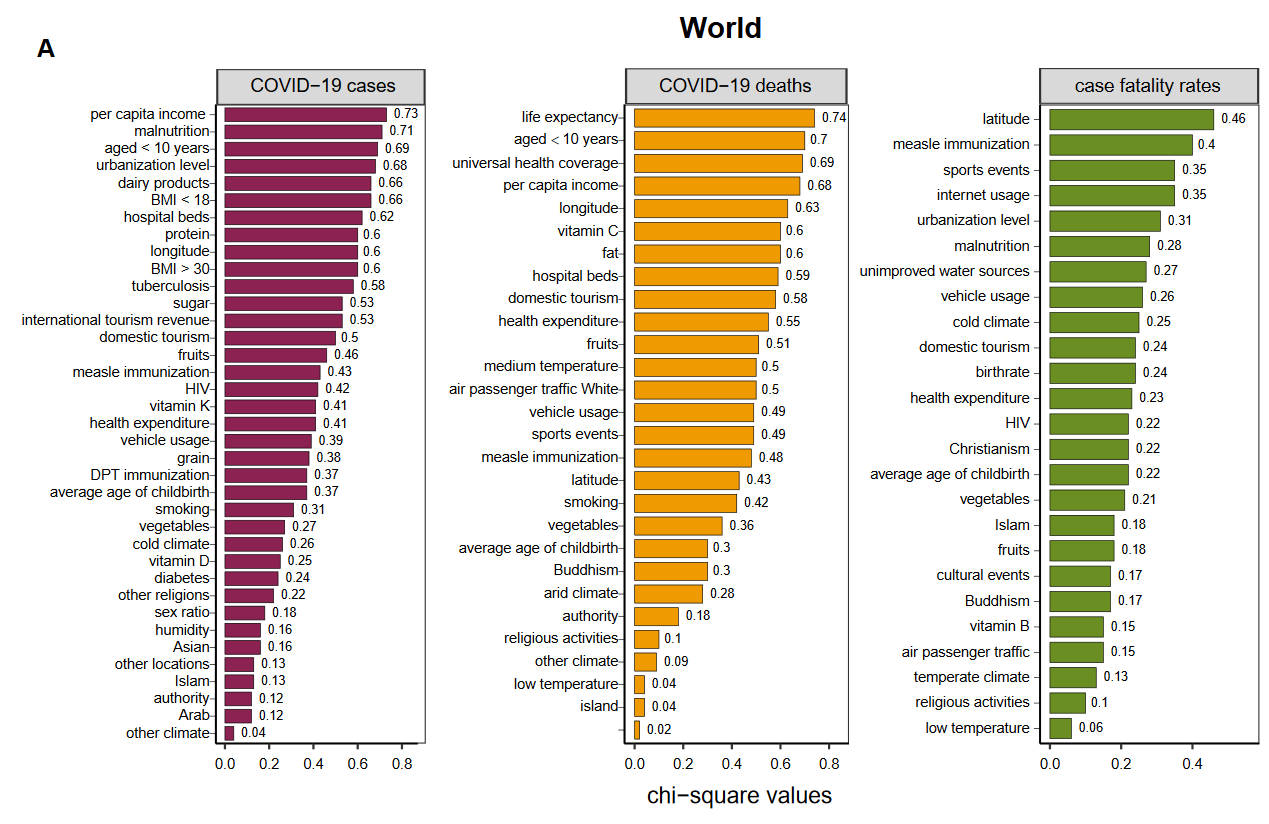
The COVID-19 virus has infected millions of people and resulted in hundreds of thousands of deaths worldwide. By using the logistic regression model, we identified novel critical factors associated with COVID19 cases, death, and case fatality rates in 154 countries and in the 50 U.S. states. Among numerous factors associated with COVID-19 risk, we found that the unitary state systemwas counter-intuitively positively associated with increased COVID-19 cases and deaths. Blood type B was a protective factor for COVID-19 risk, while blood type A was a risk factor. The prevalence of HIV, influenza and pneumonia, and chronic lower respiratory diseases was associated with reduced COVID-19 risk. Obesity and the condition of unimproved water sources were associated with increased COVID-19 risk. Other factors included temperature, humidity, social distancing, smoking, and vitamin D intake. Our comprehensive identification of the factors affectingCOVID-19 transmission and fatality may provide new insights into the COVID-19 pandemic and advise effective strategies for preventing and migrating COVID-19 spread.
Keywords
COVID-19 transmission; COVID-19fatality; risk factor; protective factor; machine learning.
All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted medRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. The copyright holder for this preprintthis version posted June 12, 2020. ; https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.10.20127472doi: medRxiv preprint
